Using prompt databases for natural language generation offers several benefits. These databases provide a wide range of pre-existing prompts that can be used as starting points for generating text. This saves time and effort in coming up with new prompts from scratch. Prompt databases also offer a variety of prompt styles, topics, and structures, allowing for diverse outputs. They provide inspiration and serve as valuable resources for generating high-quality and contextually relevant text.
Improving Language Generation with Prompt Databases
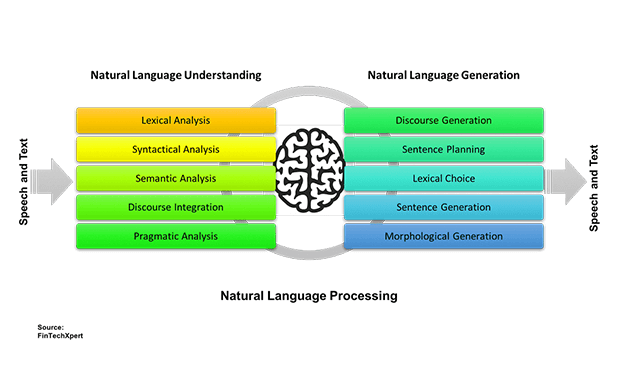
- Generating Coherent Text: Prompt databases provide pre-defined templates and prompts that help NLG models generate more coherent and contextually appropriate text. By using prompts that align with the desired output, NLG systems can produce text that flows naturally and makes logical sense.
- Handling Domain-Specific Language: Prompt databases can include domain-specific prompts and examples, enabling NLG models to generate text that is specific to particular industries or fields. This is particularly useful when generating content for specialized domains like finance, healthcare, or technology, as it ensures the generated text uses relevant terminology and reflects the specific language of that domain.
- Enhancing Language Diversity: Prompt databases can encompass a wide range of writing styles, genres, and tones. By leveraging this diversity, NLG models can generate text that caters to different contexts and user preferences. For example, prompt databases can include prompts for formal or informal language, persuasive writing, storytelling, or technical explanations, allowing NLG systems to adapt their output accordingly.
- Guiding Sentiment and Tone: Prompt databases can provide prompts that guide the sentiment or tone of the generated text. By incorporating prompts that specify the desired emotional tone (such as positive, neutral, or negative), NLG models can produce text that aligns with the intended sentiment. This is particularly useful in applications like chatbots or customer support systems, where maintaining a specific tone is crucial.
- Addressing Bias and Fairness: Prompt databases can include guidelines to address bias and promote fairness in generated text. By incorporating prompts that encourage inclusive language and discourage biased content, NLG systems can generate text that is more equitable and unbiased. This helps in avoiding discriminatory or offensive language in the generated output.
- Personalization and Customization: Prompt databases can include prompts that allow for user personalization and customization. By incorporating variables or placeholders in the prompts, NLG models can dynamically insert user-specific information or tailor the output based on user preferences. This helps in creating more personalized and engaging content.
- Rapid Iteration and Feedback: Prompt databases enable NLG developers to iterate quickly and receive feedback on the generated text. By experimenting with different prompts and incorporating user feedback, developers can refine and improve the language generation process. This iterative approach ensures that the NLG system generates higher-quality and more relevant text over time.
Harnessing Prompt Databases for Personalization
Prompt databases can be effectively harnessed for personalization in natural language generation (NLG) systems. By leveraging the capabilities of prompt databases, NLG models can generate text that is tailored to individual users, leading to a more engaging and personalized user experience. Here’s how prompt databases can facilitate personalization:
- User-Specific Information: Prompt databases can include placeholders or variables that allow for the dynamic insertion of user-specific information. For example, prompts can include placeholders for names, locations, preferences, or any other relevant user data. By incorporating this information into the generated text, NLG models can create personalized content that directly addresses the user.
- Adaptive Language Style: Prompt databases can encompass a range of writing styles, tones, or genres. By using prompts that align with the user’s preferences or the desired context, NLG systems can generate text that matches the user’s preferred style. For instance, if a user prefers a formal tone, the NLG model can be guided by prompts that reflect that preference.
- Recommendations and Suggestions: Prompt databases can include prompts that provide recommendations or suggestions based on user preferences, history, or interactions. NLG models can utilize these prompts to generate personalized recommendations, product suggestions, or content tailored to the user’s specific interests. This enhances the user experience by offering relevant and personalized information.
- Contextual Responses: Prompt databases can guide NLG models in generating responses that are contextual to the ongoing conversation or user query. By incorporating prompts that consider the previous interactions or contextual cues, NLG systems can produce more relevant and personalized responses. This fosters a sense of continuity and engagement in the conversation.
- Adaptive Tone and Sentiment: Prompt databases can include prompts that guide the sentiment or emotional tone of the generated text. By taking into account the user’s preferences or the desired emotional response, NLG models can generate text that aligns with the user’s mood or the intended sentiment of the interaction. This helps in creating a more empathetic and personalized conversational experience.
- User Feedback Integration: Prompt databases can be continuously improved by incorporating user feedback. By gathering user feedback on the generated text, NLG developers can update the prompt database to better reflect user preferences and expectations. This iterative process allows for ongoing personalization and refinement of the language generation system.
Utilizing Prompt Databases for Domain-Specific Writing
Prompt databases can be a valuable resource for generating domain-specific writing in natural language generation (NLG) systems. By harnessing the power of prompt databases, NLG models can generate text that is specific to particular industries, fields, or specialized domains. Here’s how prompt databases can be utilized for domain-specific writing:
- Industry-Specific Terminology: Prompt databases can include prompts that incorporate industry-specific terminology, jargon, or technical terms. By leveraging these prompts, NLG models can generate text that aligns with the language used in a specific domain. This ensures that the generated content is accurate, relevant, and resonates with professionals or enthusiasts in that industry.
- Field-Specific Guidelines: Prompt databases can provide field-specific guidelines or templates that help NLG models adhere to the standards and conventions of a particular domain. These guidelines may include formatting instructions, citation styles, or specific writing structures commonly used in that field. By incorporating these guidelines, NLG systems can produce text that adheres to the norms of the industry or domain.
- Subject Matter Expertise: Prompt databases can be developed in collaboration with subject matter experts (SMEs) who possess deep knowledge and expertise in a specific domain. By involving SMEs in creating the prompts, NLG models can benefit from their insights and ensure the generated text accurately reflects the nuances and intricacies of the domain. This helps in producing content that is reliable, credible, and valued by users in that field.
- Context-Specific Prompts: Prompt databases can provide context-specific prompts that cater to different use cases within a particular domain. For instance, in healthcare, prompts can cover various scenarios such as medical diagnoses, treatment plans, or patient education. By using these context-specific prompts, NLG models can generate text that is tailored to the specific requirements of the industry, ensuring accuracy and relevance.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Certain industries have strict compliance and regulatory requirements. Prompt databases can include prompts that address these requirements, ensuring that the generated text adheres to the necessary guidelines. This is particularly crucial in domains such as finance, legal, or healthcare, where accuracy and compliance are paramount.
- Customization for Different Sectors: Prompt databases can be customized for different sectors within a domain. For example, within the technology domain, prompts can be tailored for software development, cybersecurity, or data analytics. By providing sector-specific prompts, NLG models can generate text that caters to the specific needs and challenges of different sectors within the domain.
- Continuous Updates and Feedback: Prompt databases can be updated and refined based on user feedback and evolving industry practices. By incorporating user feedback and staying up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in the domain, prompt databases can ensure that the generated text remains relevant and aligned with the current industry landscape.
Ethical Considerations of Using Prompt Databases
The utilization of prompt databases in natural language generation (NLG) systems raises important ethical considerations that should be taken into account. Here are some key ethical considerations when using prompt databases:
- Bias and Fairness: Prompt databases may inadvertently contain biases or reflect societal biases present in the data used to create them. NLG models trained on biased prompt databases can perpetuate or amplify these biases in the generated text. It is crucial to carefully curate prompt databases, ensuring inclusivity, diversity, and fairness, and regularly evaluate and mitigate bias during the training and testing processes.
- Privacy and Data Protection: Prompt databases may contain sensitive or personal information, especially if they incorporate user-specific details. Care must be taken to handle and protect this data appropriately. NLG developers should ensure compliance with data protection regulations, anonymize or aggregate data when possible, and obtain informed consent from users if personal information is used in prompt databases.
- Transparency and Accountability: It is important to be transparent about the use of prompt databases and the extent to which they influence the generated text. Users should be informed about the data sources, guidelines, and potential biases present in prompt databases. Additionally, NLG developers and organizations should take responsibility for the content generated by their systems and be accountable for any potential negative impact it may have.
- Contextual Understanding and Accuracy: Prompt databases may not capture the full context of a given situation or user query. NLG models trained on prompt databases might generate text that lacks accuracy or fails to fully comprehend the nuances of a specific scenario. NLG developers should be mindful of these limitations and ensure that the generated text is factually correct, relevant, and appropriate for the intended purpose.
- User Empowerment and Control: NLG systems utilizing prompt databases should prioritize user empowerment and control over the generated content. Users should have the ability to customize or provide feedback on the prompts used, enabling them to shape the output according to their preferences. Additionally, clear mechanisms for opt-in or opt-out of personalized prompts or data usage should be provided to respect user autonomy.
- Continual Monitoring and Evaluation: Prompt databases should undergo regular monitoring and evaluation to identify and rectify any ethical concerns that may arise. This includes ongoing assessments of bias, fairness, and accuracy in the generated text. NLG developers should actively engage in feedback loops with users and experts to ensure prompt databases align with ethical standards and promote positive societal outcomes.
The rise of natural language generation
- Improved Efficiency: Prompt databases provide pre-defined templates, prompts, or examples that can be used as a starting point for generating natural language text. This saves time and effort for NLG developers as they don’t have to start from scratch. They can leverage existing prompts and modify them as per their specific requirements, leading to increased efficiency in the development process.
- Consistency: With prompt databases, NLG systems can maintain consistency in the generated text. By using standardized prompts or templates, developers can ensure that the generated content aligns with predefined guidelines, tone, style, or formatting. This is particularly useful in applications where consistency is crucial, such as generating product descriptions or customer support responses.
- Reduced Bias: Prompt databases can be designed to include guidelines that mitigate bias in generated text. By incorporating inclusive language and addressing potential biases upfront, NLG systems can generate more fair and unbiased content. This is especially important when creating text for sensitive topics or user-facing applications to ensure a more inclusive experience for all users.
- Increased Flexibility: Prompt databases provide a wide range of examples and templates that cover different contexts, styles, or genres of text. NLG developers can leverage this diversity to generate content that aligns with specific use cases. Whether it’s generating news articles, social media posts, or scientific reports, prompt databases offer flexibility in adapting to various domains and writing styles.
- Faster Iteration: NLG systems using prompt databases allow for rapid prototyping and iteration. Developers can experiment with different prompts, modify existing ones, or combine multiple prompts to generate different variations of the text. This iterative process enables quicker refinement and improvement of the generated content, leading to faster development cycles.
- Enhanced Quality Assurance: Prompt databases can include a range of high-quality examples, ensuring that the generated text meets desired standards. By using prompts that have been reviewed and validated, NLG systems can produce more accurate and reliable content. This helps in reducing errors and enhancing the overall quality of the generated text.
- User Guidance: Prompt databases can include specific guidelines or instructions for generating text in different contexts. This helps NLG systems understand user intents more effectively and generate text that aligns with user expectations. By providing clear prompts and instructions, NLG systems can produce more relevant and context-aware responses, improving the user experience.
Understanding Prompt Databases
Prompt databases are repositories of pre-defined templates, prompts, or examples that are used as a resource for natural language generation (NLG) systems. These databases are designed to provide guidance and structure for generating human-like text.
Prompt databases serve as a starting point for NLG developers, offering a collection of text snippets or prompts that represent desired output or writing styles. Developers can leverage these prompts and modify them to suit their specific requirements, saving time and effort in the development process.
The prompts in these databases can cover a wide range of topics, contexts, and writing styles. They can include examples for generating product descriptions, customer support responses, news articles, social media posts, scientific reports, and more. By utilizing prompt databases, developers have access to a diverse set of templates that cater to different domains and genres of text.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prompt databases offer significant benefits for natural language generation (NLG) systems. They serve as a valuable resource for developers, providing pre-defined templates, prompts, and examples that guide the generation of human-like text. Prompt databases enhance language generation by ensuring coherence, addressing domain-specific language, promoting diversity, guiding sentiment and tone, mitigating bias, enabling personalization, and facilitating rapid iteration.
References:
